|
TOXOPLASMOSIS & PREGNANCY

WHAT IS TOXOPLASMOSIS?
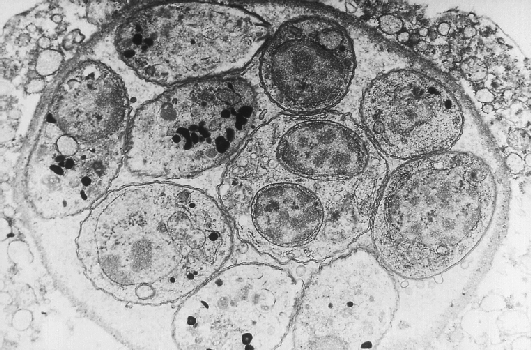
Electron micrograph of a Toxoplasma gondii tissue cyst
(Photocredit: CDC Public Health Image Library)
Toxoplasmosis is the disease syndrome caused by a protozoan organism called Toxoplasma gondii. It affects most animals (most notably sheep, cats, and humans), but even insects, fish, and earthworms may be carriers. Because of the risk to an unborn child, many medical doctors go so far as to recommend that pregnant women do not keep cats as pets.
|

(Photocredit: Morguefile.com)
|

(Photocredit: Morguefile.com)
|

(Photocredit: Morguefile.com)
|
|
A human with an acute Toxoplasma infection experiences varying degrees of illness: fever, swollen lymph nodes, muscle stiffness, joint pain, swollen liver and/or spleen (manifested as a sore upper abdomen). These symptoms may be so mild as to go unnoticed. Illness lasts 1-12 weeks and is often dismissed as a bad cold or mononucleosis.
However, if the person infected is a pregnant woman, the Toxoplasma organism may cross the placenta. The amount of damage done depends on the stage of pregnancy at the time of infection. Infection in early pregnancy may result in miscarriage or stillbirth. Infection in mid-pregnancy may result in a child with varying degrees of blindness (due to inflamed retina - the most common result of congenital infection) and/or various severe neurological conditions including hydrocephalus or microcephaly. Sometimes problems are not evident at birth and show up later in life.
|

(Photocredit: Public Domain Image U.S. Dept of Agriculture)
|
The problems described above occur only when a woman is infected with Toxoplasma for the first time and it so happens that she is pregnant at the time of that first infection or if she is immune-suppressed by AIDs or cancer therapy. In other words, a woman with a normal immune system who has already had the infection is not likely to get sick again nor is she likely to transmit the organism to an unborn child. (It is estimated that one third of the U.S. population has already had Toxoplasmosis.)
If you get infected during pregnancy, antibiotics can be used to stop the infection. Testing is generally part of a pre-natal evaluation.
HOW DO PEOPLE GET THIS DISEASE?
|
There are two basic forms of Toxoplasma organism: the "oocyst," which is shed in the cat feces, and the Toxoplasma tissue stages, which live in the flesh of such food animals as hogs and lambs. A person who inadvertently eats either of these forms of Toxoplasma is liable to become infected. Raw goat’s milk is also an important source of infection.
When might one inadvertently consume an oocyst? Usually by putting a contaminated hand or finger in one's mouth. Where would a hand get contaminated? Changing a litter box used by an actively infected cat, gardening or handling soil contaminated by the feces of an actively infected cat, or touching cat feces that is at least a day or two old. A cat must be in an active stage of infection to transmit the infection to you.
|
 (Photocredit: Ocdp via Wikimedia Commons) (Photocredit: Ocdp via Wikimedia Commons) |
|
When might one inadvertently consume a Toxoplasma tissue stage? Tasting meat while it is cooking, eating under cooked meat, handling raw meat and getting tissue in one's mouth accidentally, eating food prepared on a cutting board contaminated with raw meat.
Washing one's hands regularly, wearing gloves while gardening, and having someone else change the litter box can eliminate infection. Most people are infected by eating under-cooked meats.
|
 (Photocredit: Morguefile.com) (Photocredit: Morguefile.com) |
IF A CAT HAS AN ACTIVE TOXOPLASMA INFECTION, WON'T HE BE OBVIOUSLY SICK?
Not necessarily. Feline toxoplasmosis can be as subtle as the human version. Cats get infected by hunting and eating prey, eating raw food diets, or by inadvertently licking oocysts during grooming. When the cat gets infected, the early stages involved an "intestinal form" where the contagious oocysts are shed in feces but the cat may or may not have any diarrhea.
HOW IS MY CAT A RISK TO ME?
|

(Photocredit: CDC Public Health Image Library)
|
The cat has probably been over-emphasized as a carrier of Toxoplasma; most human infections result from eating tissue stages of Toxoplasma in undercooked meat.
Usually a cat will only shed oocysts after the first infection of Toxoplasma; a cat that has already had a Toxoplasma infection usually will not re-shed the oocysts unless its immune system has been compromised (as through the feline leukemia virus infection or drugs.) Cats shedding oocysts generally do so for 5-14 days.
Oocysts require 24-48 hours to sporulate --- that is, grow into a form which is dangerous to people. For this reason, the cat's litter box should be changed daily or twice daily so the cysts will be thrown out before they reach an infectious stage. Dangerous oocysts can be contacted when gardening. Note that freezing weather will not reliably kill dangerous oocysts in soil nor will freezing meat kill the dangerous tissue forms.
Dogs that eat cat feces can also shed oocysts that they have eaten for 2 days.
Your cat may be tested to see if he/she has already had Toxoplasmosis; a cat that has already been infected is unlikely to shed dangerous oocysts in the future.
The cat itself is not a source of oocyts, only its feces are.
|
HOW CAN I AVOID INFECTION?
- Probably the most important thing is to be careful when cooking raw meat, especially lamb and pork. Wash your hands after handling meat. Remember that microwaving does not heat evenly enough to reliably kill the organism.
DO NOT EAT MEAT OR TASTE MEAT BEFORE IT IS FINISHED COOKING.
- Wash your hands after handling your cat and his/her litter box.
- Do not allow your cat to eat raw meat. Feed only commercial cat food and do not allow your cat outside to hunt.
- Change the litter box daily or twice daily. It is best of course, if someone else changes the box while you are pregnant.
- Do not dump the litter box into the backyard. Always wear rubber gloves when gardening.
- Do not allow the cats access to barns where food animals are kept. This is how food animals get infected.
- Do not drink raw milk, especially goat's milk.
Although it is possible to get Toxoplasmosis from cats, no correlation has been found between cat ownership and Toxoplasma infection. There is, however, a very strong association between Toxoplasma infection and working with raw meat as in a slaughterhouse or as a butcher. Be careful handling raw meat.
FOR MORE TOXOPLASMOSIS INFORMATIONAL SITES:
www.cdc.gov/parasites/toxoplasmosis/gen_info/pregnant.html
www.webmd.com/baby/toxoplasmosis#1
Printer Friendly Version
(PDF Format)

Page last updated: 6/17/2019
|